ABSTRACTA vertical tube furnace with a window allows to observe the formation and growth of single crystals from the gaseous phase in a conical end of a sealed fused silica ampoule. A quantitative description of nucleation and crystal growth is obtained by a sudden or continuous change of the capsule position in a fixed temperature distribution. Supersaturations for seed formation and crystal growth are reliably estimated from the measured temperature profile. The morphology of a growing crystal surface indicates the importance of the two kinetic processes which follow successively. Polyhedral forms results from a slow surface incorporation kinetics and fast mass transfer in the gaseous phase, whereas a rounded interface is caused by a slow mass transfer and a fast incorporation kinetics. For a small sudden alternation of the supersaturation, the crystal length relaxes exponentially with time. The time constant is a linear function of the final crystal length 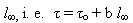 where τ0 is determined by the incorporation kinetics and b by the mass transfer. The functional relation between the change of supersaturation (input function) and crystal length (response) can be explained by the theory of systems. Three crystal growth systems are presented which differ in the formation of the gaseous phase: (a) Congruent sublimation with the examples iodine, GeS, and C60, (b) dissociative sublimation with the example of ZnSe and (c) chemical reaction with the example Ge(s) + Gel4(g) =2Gel2(g). where τ0 is determined by the incorporation kinetics and b by the mass transfer. The functional relation between the change of supersaturation (input function) and crystal length (response) can be explained by the theory of systems. Three crystal growth systems are presented which differ in the formation of the gaseous phase: (a) Congruent sublimation with the examples iodine, GeS, and C60, (b) dissociative sublimation with the example of ZnSe and (c) chemical reaction with the example Ge(s) + Gel4(g) =2Gel2(g). |

